HEC-RAS Flood Modeling for Hydraulic Flood Analysis
HEC-RAS Flood Modeling: Comprehensive Guide to Hydraulic Flood Analysis
HEC-RAS flood modeling has become the industry standard for hydraulic flood analysis across infrastructure projects, river management studies, and disaster preparedness planning. This powerful tool enables engineers and consultants to simulate water flow behavior in rivers, channels, and floodplains with remarkable accuracy.
Understanding how water behaves during flood events is critical for protecting lives, infrastructure, and investments. HEC-RAS provides the computational framework needed to analyze complex hydraulic conditions and predict flood extents, depths, and velocities under various scenarios.
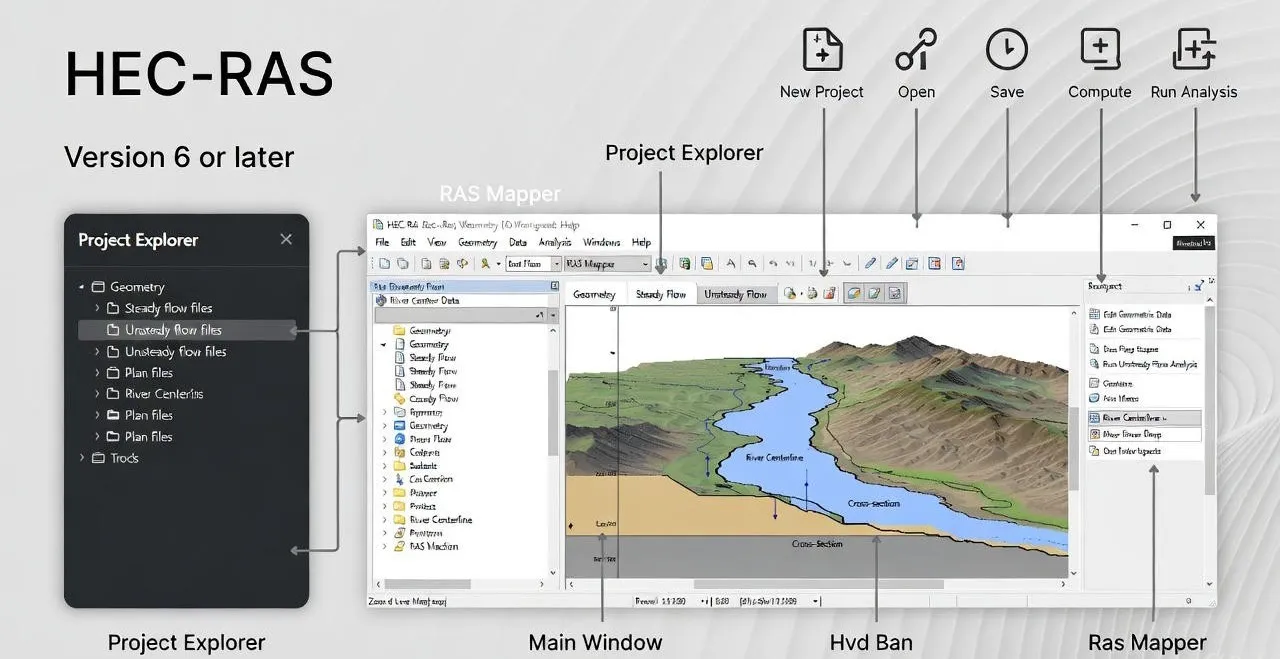
What is HEC-RAS?
HEC-RAS (Hydrologic Engineering Center's River Analysis System) is a comprehensive hydraulic modeling software developed by the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers (USACE). Since its initial release, the software has evolved from a one-dimensional steady flow model to a sophisticated tool capable of complex two-dimensional unsteady flow simulations.
The software performs hydraulic calculations for full networks of natural and constructed channels. It provides engineers with the ability to model water surface profiles, evaluate floodplain encroachment, design hydraulic structures, and assess flood damage potential.
HEC-RAS is freely available, well-documented, and widely accepted by regulatory agencies worldwide. Its integration capabilities with GIS platforms make it an essential tool in modern flood risk management workflows.
Why HEC-RAS is Used for Flood Modeling
The widespread adoption of HEC-RAS flood modeling stems from several key advantages that make it the preferred choice for hydraulic flood analysis:
- 1. Industry Acceptance: Government agencies, consulting firms, and academic institutions recognize HEC-RAS outputs for regulatory submissions, Detailed Project Reports (DPRs), and environmental impact assessments.
- 2. Computational Accuracy: The software employs robust numerical methods to solve complex hydraulic equations, providing reliable results when properly calibrated with field data.
- 3. Cost-Effectiveness: Being freely available software eliminates licensing costs while maintaining professional-grade capabilities.
- 4. Versatility: From small drainage channels to major river systems, HEC-RAS handles projects of all scales effectively.
- 5. GIS Integration: Seamless connectivity with GIS platforms like ArcGIS enables efficient data preparation and result visualization.
- 6. Technical Support: Extensive documentation, training materials, and active user communities provide ongoing technical assistance.
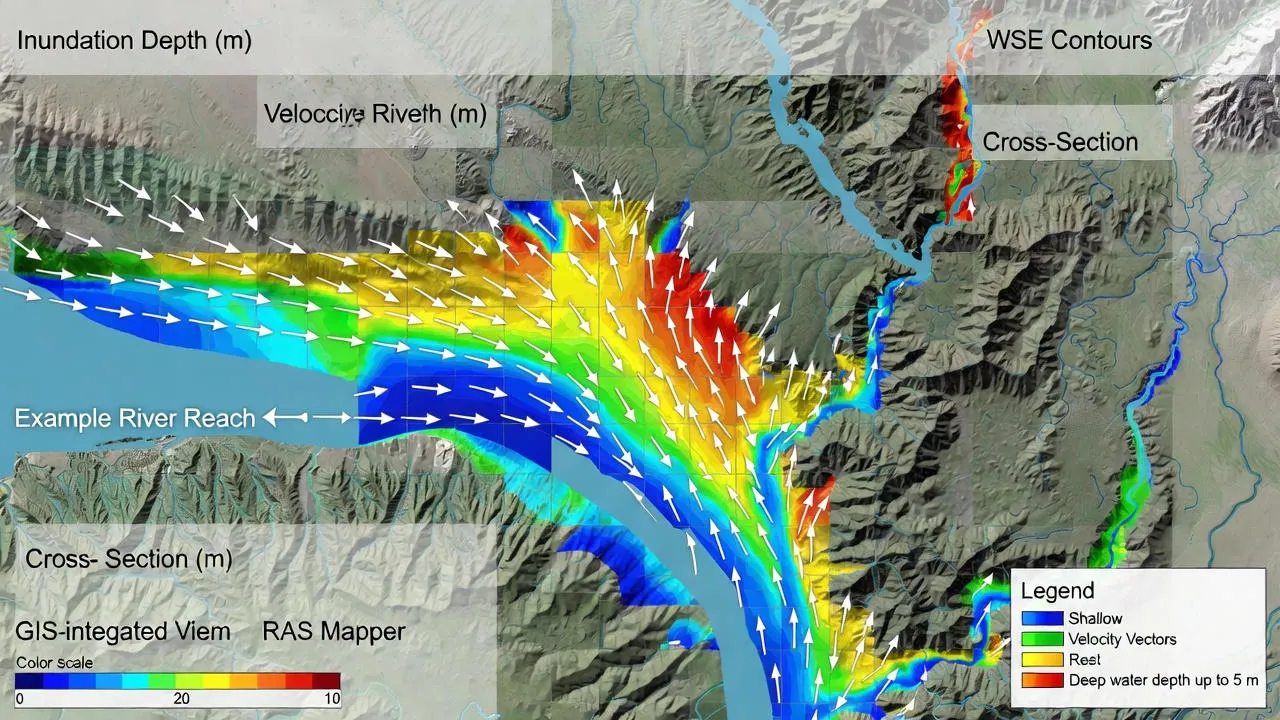
Types of Flood Modeling in HEC-RAS
HEC-RAS offers multiple modeling approaches to suit different project requirements and site conditions. Understanding these options helps engineers select the most appropriate method for their specific application.
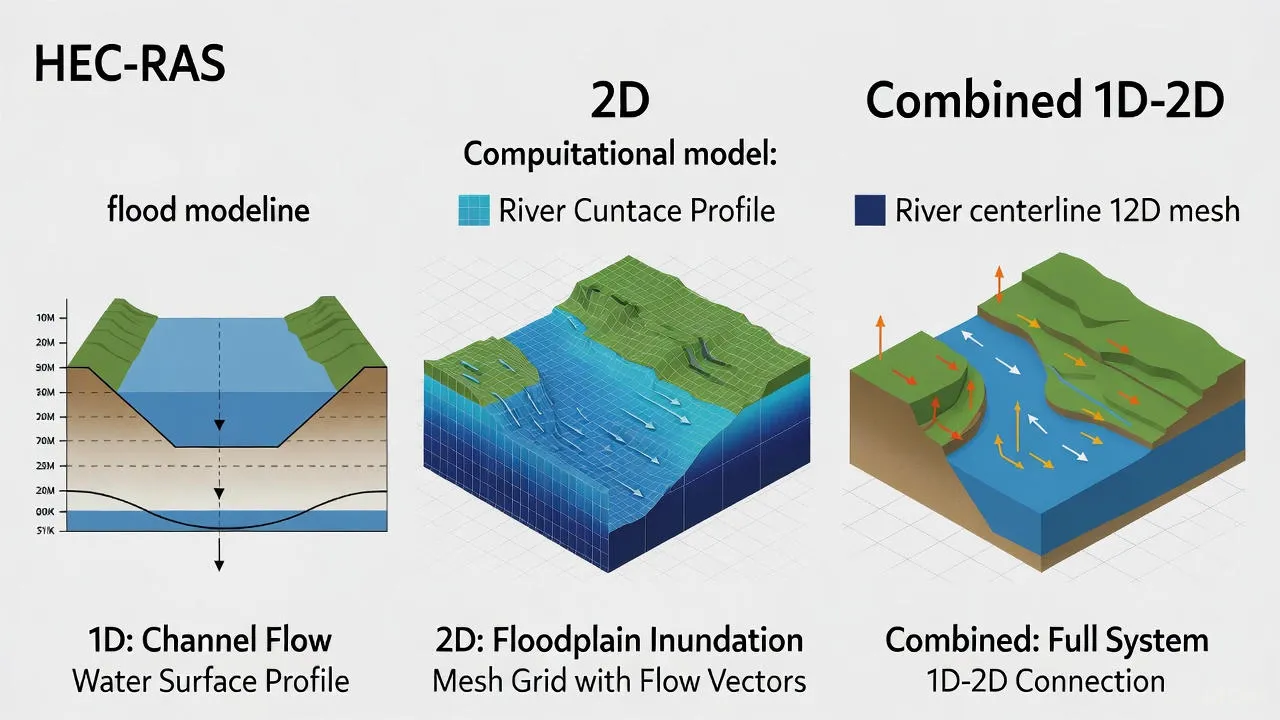
1D Flood Modeling
One-dimensional modeling in HEC-RAS analyzes water flow along a channel centerline using cross-sectional geometry. This approach works well for rivers and channels where flow is predominantly in one direction.
Applications include river reach analysis, bridge hydraulics, culvert design, and floodplain delineation along defined channels. The 1D approach is computationally efficient and requires less detailed terrain data, making it suitable for preliminary studies and long river reaches.
2D Flood Modeling
Two-dimensional modeling simulates water flow across a continuous surface using a computational mesh. This method captures lateral flow patterns, floodplain inundation, and complex flow behaviors that 1D models cannot represent.
Urban flooding studies, coastal inundation analysis, dam break scenarios, and areas with significant lateral flow benefit from 2D modeling capabilities. The approach requires high-resolution terrain data and more computational resources but provides detailed spatial flood information.
Combined 1D-2D Approach
Many real-world projects benefit from combining both approaches. Rivers can be modeled in 1D while floodplains and urban areas use 2D representation. This hybrid method optimizes computational efficiency while maintaining accuracy where spatial detail matters most.
Key Inputs Required for HEC-RAS Flood Modeling
Accurate flood modeling depends on quality input data. The following elements form the foundation of any HEC-RAS flood model:
- 1. River Geometry: Channel alignment, cross-section locations, and geometric properties define the flow conveyance system.
- 2. Cross-Sections: Detailed measurements of channel and floodplain elevations at regular intervals along the river.
- 3. Flow Data: Historical discharge records, design flood hydrographs, or rainfall-runoff model outputs.
- 4. Boundary Conditions: Upstream flow conditions and downstream water levels or rating curves.
- 5. Digital Elevation Model (DEM): High-resolution terrain data for floodplain representation, especially critical for 2D modeling.
- 6. Manning's Roughness Coefficients: Parameters representing channel and floodplain surface resistance to flow.
- 7. Hydraulic Structures: Bridges, culverts, weirs, and other structures affecting flow patterns.
- 8. Land Use Data: Information on vegetation, development, and surface characteristics affecting flow resistance.
HEC-RAS Flood Modeling Process
Successful hydraulic flood analysis using HEC-RAS follows a systematic workflow that ensures model reliability and defensible results.
Step 1: Data Preparation
Collect and process all required input data. Survey data is cleaned and formatted. DEM is processed to remove artifacts and ensure proper drainage network representation. GIS data layers are prepared for import into HEC-RAS.
Step 2: Model Setup
The geometric data is entered into HEC-RAS, including river reaches, cross-sections, and hydraulic structures. Flow data and boundary conditions are specified. Manning's n values are assigned based on field observations and land use characteristics.
Step 3: Model Calibration
When historical flood data is available, the model is calibrated by adjusting parameters until simulated water levels match observed flood marks or gauge data. This validation step establishes confidence in model predictions.
Step 4: Simulation Runs
Multiple scenarios are run representing different flood return periods (10-year, 25-year, 50-year, 100-year events) or climate-driven extreme conditions. Unsteady flow analysis may be used for time-varying flood events.
Step 5: Result Interpretation
Water surface profiles, velocity distributions, and inundation maps are analyzed. Critical areas of high flood risk are identified. Results are exported to GIS for visualization and further spatial analysis.
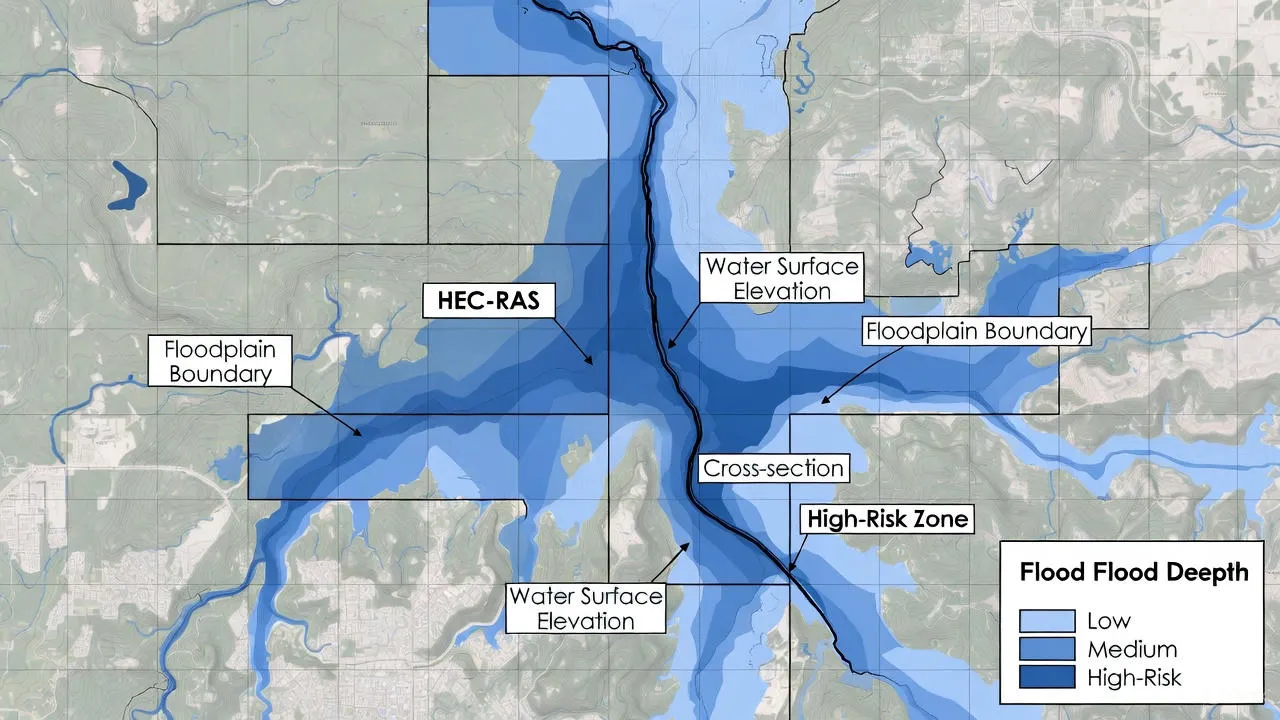
Applications of HEC-RAS Flood Modeling
HEC-RAS hydraulic modeling serves diverse applications across infrastructure development and flood risk management:
Urban Flood Studies
Cities use HEC-RAS to analyze drainage system capacity, identify flooding hotspots, and plan infrastructure improvements. The 2D modeling capability accurately represents urban flow patterns around buildings and through street networks.
Highway and Bridge Projects
Transportation projects require hydraulic analysis to design adequate bridge openings, evaluate scour potential, and ensure road elevations remain above flood levels. HEC-RAS modeling supports these critical design decisions.
River Training Works
River management projects including embankments, revetments, and channel modifications are evaluated using HEC-RAS to predict flow behavior and assess effectiveness of proposed interventions.
Floodplain Zoning
Regulatory agencies use floodplain mapping from HEC-RAS to delineate flood zones for land use planning, building code enforcement, and insurance rate determination.
Disaster Management Planning
Emergency planners rely on HEC-RAS flood simulations to identify evacuation routes, position emergency resources, and develop flood response protocols.
Dam Safety and Impact Studies
Dam break scenarios and reservoir operations are modeled to understand downstream flood impacts and develop emergency action plans.

Benefits of Using HEC-RAS for Flood Modeling
Organizations adopting HEC-RAS flood modeling gain significant advantages in their flood risk management programs:
- 1. Enhanced Risk Understanding: Quantitative flood depth, velocity, and extent data enables risk-based decision making rather than relying on historical experience alone.
- 2. Informed Planning: Infrastructure can be positioned optimally, avoiding high-risk zones while maintaining functional requirements.
- 3. Damage Reduction: By identifying vulnerable areas before construction, projects incorporate protective measures that minimize flood damage.
- 4. Regulatory Compliance: Professional HEC-RAS analysis satisfies environmental clearance requirements and supports permit applications.
- 5. Cost Savings: Optimizing designs based on actual flood behavior prevents over-engineering while ensuring adequate protection.
- 6. Stakeholder Communication: Visual flood maps and animations help communicate risks to non-technical audiences, building support for flood mitigation investments.
Limitations and Best Practices
While powerful, HEC-RAS flood modeling requires careful application to ensure reliable results. Understanding limitations helps practitioners avoid common pitfalls.
Data Quality Dependency
Model accuracy directly reflects input data quality. Poor survey data, outdated DEMs, or inadequate flow records produce unreliable results regardless of sophisticated modeling techniques. Invest in quality data collection for projects requiring high confidence levels.
Need for Expert Handling
HEC-RAS requires trained users who understand hydraulic principles, numerical methods, and model limitations. Results should be reviewed by experienced hydraulic engineers before use in design or planning decisions.
Calibration Importance
Whenever possible, calibrate models against observed flood data. Uncalibrated models may produce plausible but inaccurate results. Document assumptions clearly when calibration data is unavailable.
Appropriate Method Selection
Choose modeling approaches suited to the problem. Simple 1D analysis may suffice for some applications while others require 2D representation. Over-complicating models wastes resources while oversimplifying compromises accuracy.
Sensitivity Analysis
Test how results respond to input parameter variations. Understanding model sensitivity to Manning's n values, boundary conditions, or mesh resolution builds confidence and identifies areas requiring field verification.
Conclusion
HEC-RAS flood modeling has established itself as an indispensable tool in modern hydraulic engineering and flood risk management. Its combination of sophisticated computational capabilities, industry acceptance, and accessibility makes it the first choice for professionals conducting hydraulic flood analysis.
From preliminary feasibility studies to detailed design and disaster planning, HEC-RAS provides the analytical foundation for informed decision-making. As climate change increases flood risks and urban development pressures mount, the role of robust flood modeling using HEC-RAS becomes even more critical.
Success with HEC-RAS flood modeling depends on quality input data, appropriate methodology selection, proper calibration when possible, and expert interpretation of results. Organizations investing in these fundamentals gain powerful capabilities to understand, communicate, and mitigate flood risks effectively.
Whether you're planning infrastructure, managing river systems, or developing flood preparedness strategies, HEC-RAS offers the technical capabilities needed to address today's complex hydraulic challenges with confidence and precision.
Why Choose Bhoojal Survey for HEC-RAS Flood Modeling?
At Bhoojal Survey, we combine advanced HEC-RAS hydraulic modeling expertise with comprehensive field data collection and GIS capabilities. Our multidisciplinary team has successfully delivered flood modeling projects across diverse applications including highways, urban drainage, river management, and infrastructure planning.
We provide end-to-end services from topographic survey and data collection through model development, calibration, scenario analysis, and deliverable preparation. Our HEC-RAS models meet regulatory requirements and support confident engineering decisions backed by rigorous technical analysis.
Call +91-96918 58058
