Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering: Complete 2026 Guide
- Home
- Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering

Why Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering Matters More Than Ever in 2026
Water is fast becoming one of the most critical resources on the planet. Across India and much of the world, the combination of rapid urbanization, unpredictable monsoon patterns, prolonged droughts, and aging infrastructure has put enormous pressure on how we manage, distribute, and conserve water. In this context, hydrology and water resources engineering has emerged as one of the most important disciplines shaping modern infrastructure and sustainable development.
The key challenges making this field critical today include:
- Climate change is actively altering rainfall patterns, intensifying floods, and accelerating aquifer depletion.
- Cities are expanding faster than drainage systems can handle, creating serious stormwater risks.
- Agricultural zones face constant uncertainty around irrigation planning and seasonal water availability.
- Aging water infrastructure is failing to meet the demands of a rapidly growing population.
Hydrology and water resources engineering provides the scientific foundation that guides everything from designing a stormwater drain in a new township to assessing the viability of a large reservoir — making it indispensable for engineers, planners, developers, and policymakers alike.
What is Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering?
Hydrology and water resources engineering is the branch of civil and environmental engineering that deals with the scientific study of water — its occurrence, distribution, movement, and interaction with land, atmosphere, and human infrastructure. In simple terms, it answers the most important questions about water:
- Where does water come from, and where does it go?
- How much freshwater is actually available at a given location?
- How can we use water sustainably without damaging the environment?
- How do we protect infrastructure from floods, erosion, and waterlogging?
Hydrology, as a science, focuses on the water cycle — from rainfall and evaporation to river flow and groundwater recharge. Water resources engineering applies that science to build and manage infrastructure. Together they form a powerful real-world framework. Real-life examples include:
- A highway developer needing to know how much stormwater runoff a road embankment will generate during a heavy monsoon — hydrology provides the answer.
- A city planner designing a drainage network to handle a once-in-50-years flood event — water resources engineering delivers the solution.
- A dam authority assessing safe water storage capacity for a new reservoir — both hydrology and water engineering work together to get it right.
Core Areas Covered in Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering
This field covers a wide range of specializations. The most important core areas include:
● Surface Water Hydrology
- Studies rivers, streams, lakes, and ponds and how they behave during normal and extreme weather events.
- Engineers perform rainfall runoff analysis to determine how much rain actually flows into drainage channels.
- This data is essential for designing bridges, culverts, and flood embankments sized for real-world conditions.
● Groundwater Engineering
- Focuses on subsurface water, aquifer systems, recharge rates, and borewell or dewatering system design.
- An aquifer assessment determines how much water can be safely extracted without causing long-term depletion.
- Critical for both urban water supply planning and long-term agricultural sustainability.
● Flood Risk Assessment
- Combines historical rainfall data, river basin topography, and hydrological modeling.
- Identifies flood-prone areas and determines expected flood levels for engineering design purposes.
- No longer optional — it is a regulatory and practical necessity for all large development projects.
● Irrigation Planning
- Ensures canal networks, check dams, and drip systems are designed based on actual water availability and crop demand.
- Prevents both waterlogging and water shortage — two extremes that proper engineering can and must avoid.
- Watershed management supports this by managing entire river basins or catchment areas holistically.
● Urban Drainage Design and Stormwater Management
- As cities grow, impervious surfaces like roads and rooftops dramatically increase surface runoff.
- Engineers design urban drainage systems that carry stormwater safely without causing flooding or erosion.
- Stormwater management systems are now a mandatory requirement in all new urban development approvals.
Why Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering is Critical in 2026
The year 2026 presents compounding water challenges that make professional engineering more essential than ever. Here is why:
● Rapid Urbanization
- Over 30 Indian cities are significantly expanding with new industrial corridors, smart city initiatives, and residential townships.
- Each development demands reliable water supply and robust excess water management from the very start of planning.
- Professional hydrological input at the design stage prevents costly infrastructure failures during operation.
● Extreme Rainfall Events
- Flash floods in urban areas and overflowing rivers in previously safe zones are now the new normal.
- The climate change impact on water is intensifying year by year across all regions of India.
- Without proper engineering responses, the economic and human cost of flood damage will continue to escalate.
● Water Scarcity Issues
- Overextraction of groundwater, shrinking glaciers, and erratic monsoons are depleting freshwater reserves rapidly.
- Water conservation strategies and sustainable water engineering are now core planning requirements, not optional add-ons.
- Water-efficient infrastructure design is essential to meet both present and future demand responsibly.
● Tightening Regulatory Requirements
- Environmental clearances now mandate detailed hydrological impact assessments and flood risk evaluations.
- Developers who engage hydrological survey services early avoid costly approval delays and project setbacks.
- Non-compliance with drainage and stormwater norms can result in project cancellations, fines, and legal action.
Role of Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering in Infrastructure Projects
Hydrology and water resources engineering plays a foundational role across all major infrastructure categories:
● Roads and Highways
- Every road passes through natural drainage paths that must be scientifically assessed before construction.
- A thorough river basin study ensures culverts and bridges are sized to handle peak flood discharges safely.
- Undersized drainage structures lead to washouts, road closures, and expensive emergency repair costs.
● Solar and Renewable Energy Projects
- Large solar parks cover extensive land and significantly alter natural surface drainage patterns.
- Panel foundations and access roads must be positioned well outside flood-prone zones.
- Downstream drainage impacts must be assessed and mitigated to satisfy environmental clearance conditions.
● Industrial Zones
- Factories require reliable water for operations and responsible environmental water management for wastewater discharge.
- Comprehensive water supply planning ensures uninterrupted operations through both dry and wet seasons.
- Hydrological studies ensure water intake and discharge systems comply with all applicable environmental norms.
● Smart Cities
- Smart urban planning integrates hydrology through permeable pavements, green roofs, and real-time flood monitoring systems.
- Drainage system design in smart cities combines natural water management with engineered infrastructure.
- Hydrological data creates cities that are both functionally livable and genuinely climate-resilient.
● Dam and Reservoir Planning
- Dam and reservoir design is the most technically intensive area within water resources engineering.
- Structures must account for extreme rainfall, sedimentation, seismic activity, and changing upstream land use over decades.
- Errors in hydrological assessment at this scale can have catastrophic and irreversible consequences for communities.
Modern Technologies Used in Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering
Technology has completely transformed how hydrological surveys and water resource studies are conducted. Key modern tools include:
● GIS Mapping
- Overlays topographic data, land use, soil types, and rainfall records for highly accurate catchment models.
- What once required weeks of manual calculation can now be completed in hours with far greater spatial accuracy.
● Drone Survey Integration
- Drones equipped with LiDAR and multispectral sensors map river channels and drainage networks at centimeter-level precision.
- Covers large areas quickly and captures real-time field data without extensive manpower requirements.
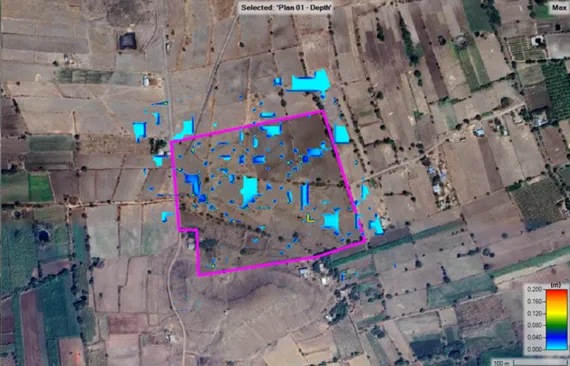
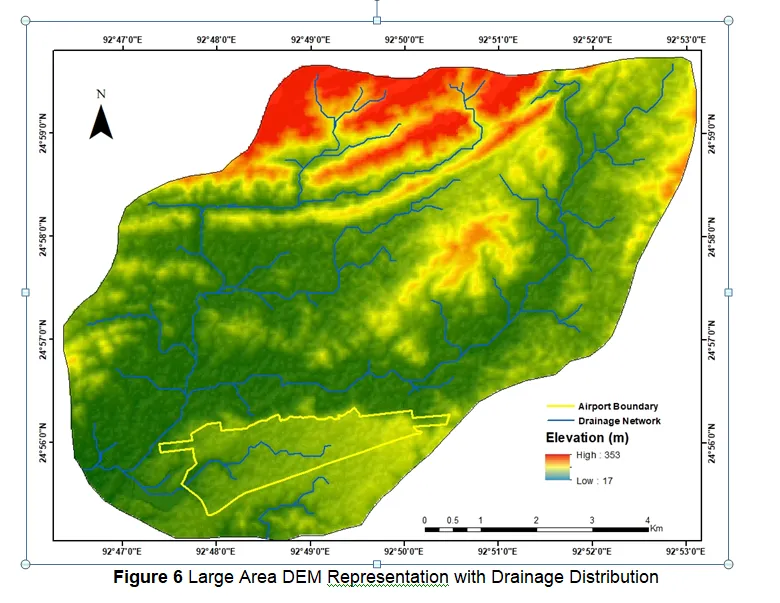
● Digital Elevation Models (DEM)
- Forms the backbone of all modern hydrological analysis, flood simulation, and drainage design work.
- Eliminates guesswork from outdated topographic maps and allows precise simulation of water flow patterns.
● Hydrological Modeling Software
- Platforms like HEC-HMS, SWMM, and MIKE FLOOD simulate complete storm events and predict flood extents accurately.
- Engineers can test multiple drainage design scenarios before any physical construction begins on site.
- Saves enormous redesign costs and significantly reduces the risk of infrastructure failure after construction.
● AI-Based Flood Prediction
- Machine learning algorithms combine rainfall data, satellite imagery, and river gauge readings for accurate early flood warnings.
- Provides greater lead time and prediction accuracy than traditional methods, especially for urban stormwater scenarios.
- Enables city authorities and infrastructure operators to take preventive action before flooding occurs.
Benefits of Professional Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering Services
Engaging professional services early in any project delivers real, measurable benefits that far outweigh the initial investment:
● Risk Reduction
- Identifies flood-prone zones, unstable drainage patterns, and groundwater risks before any construction begins.
- Allows engineers and developers to make fully informed decisions on site layout, foundation depth, and drainage design.
● Cost Efficiency
- A properly sized drainage system — not too small to fail, not too large to waste budget — requires accurate hydrological input.
- Projects that skip this step often face expensive retrofits, flood damage insurance claims, or regulatory penalties.
● Long-Term Sustainability
- Sustainable water engineering practices reduce the environmental footprint of infrastructure projects significantly.
- Rainwater harvesting, permeable surface design, and groundwater recharge planning support green building certifications.
● Regulatory Compliance
- EIA reports, CGWA NOC applications, and state drainage clearances all require documented hydrological analysis.
- Professional hydrological survey services provide the technical reports needed to clear regulatory approvals smoothly.
- Well-prepared documentation reduces back-and-forth with authorities and speeds up overall project timelines.
Hydrology vs Hydrogeology: Understanding the Clear Difference
These two terms are frequently confused. Here is a clear comparison of both disciplines:
● Hydrology and Water Resources Engineering
- Covers the entire water cycle — rainfall, surface runoff, river flow, evaporation, and groundwater interaction.
- Applies this science to design and manage water-related infrastructure at both project and catchment scale.
- Includes flood control, stormwater management, watershed management, irrigation systems, and dam design.
- Provides a broad, integrated view of all water systems across a landscape or development footprint.
● Hydrogeology
- Specifically focused on groundwater — its movement through geological formations and aquifer systems.
- A hydrogeologist typically works on borewell surveys, aquifer mapping, and groundwater contamination assessments.
- Overlaps with water resource management on groundwater recharge but does not cover surface water systems.
- Many large infrastructure projects require input from both disciplines to achieve a complete water environment picture.
How to Choose the Right Water Resources Engineering Consultant
Selecting the right consultant is critical to getting reliable results. Look carefully for these four key qualities:
● Technical Expertise
- Look for qualified civil or environmental engineers with specific training in hydrological analysis and flood modeling.
- Credentials from recognized professional bodies and a proven track record on similar project types are strong indicators.
● Field Experience
- A consultant who has conducted actual hydrological survey services across different terrain types brings irreplaceable practical insight.
- Ask specifically about completed projects in your geography — coastal, hilly, alluvial plains, or arid zones.
● Survey Equipment and Technology
- Consultants using drone-based LiDAR, advanced GIS platforms, and industry-standard modeling software deliver far more accurate outputs.
- Always ask what tools are used and exactly how field data is collected, processed, and quality-verified.
● Reporting Standards
- A good hydrological report clearly states methodology, presents data transparently, explains limitations, and gives actionable recommendations.
- Reports prepared to IS codes, CWC guidelines, or international equivalents carry more weight in regulatory submissions.
- Confirm the report format is fully compatible with the specific regulatory body you need to submit it to.
Building a Water-Resilient Future Through Engineering Excellence
The challenges facing water systems in 2026 demand a serious, science-based response. Hydrology and water resources engineering is not a support service — it is a foundational discipline that every infrastructure project needs at its core. Key takeaways for future-ready water planning:
- Climate resilience is now a design requirement, not a bonus — infrastructure planned without hydrological input is not built to last.
- The cost of ignoring water management in the early stages of a project is always far higher than the cost of getting it right from the start.
- Engineering responsibility means making decisions based on verified data and scientific evidence, not assumptions.
- Sustainable water infrastructure protects your investment, your community, and the environment for generations to come.
If your project involves land development, water supply, drainage, flood protection, irrigation, or any form of environmental clearance, engaging a qualified team for hydrology and water resources engineering is a decision that pays for itself many times over.
Ready to Plan Your Water Management Strategy?
Whether you need a flood risk assessment, urban drainage design, watershed management study, or a complete hydrological survey for your project, our team of certified water resources engineers is ready to help. We combine advanced survey technology, regional expertise, and transparent reporting to deliver results you can rely on.
Frequently Asked Questions
What does hydrology and water resources engineering include?
Hydrology and water resources engineering covers a broad range of services, including:
- Surface water analysis and detailed rainfall runoff studies
- Groundwater assessment and aquifer mapping
- Flood risk evaluation and flood plain delineation
- Stormwater management and urban drainage design
- Irrigation planning, watershed management, and dam and reservoir design
Why is it important for infrastructure projects?
Infrastructure projects interact with natural water systems in ways that can cause serious problems if not correctly managed. Professional engineering services ensure:
- Drainage systems are correctly sized for actual rainfall conditions in that specific location
- Structures are positioned safely outside identified flood-risk zones
- Projects meet all environmental clearance and applicable regulatory requirements
- Long-term operational safety is maintained across all seasonal weather conditions
How does it help in flood management?
Flood management through hydrology and water resources engineering involves several key steps:
- Using rainfall runoff analysis and river flow records to predict flood magnitude and geographic extent
- Mapping flood-prone areas precisely using Digital Elevation Models (DEM) and GIS tools
- Designing protection measures like embankments, retention basins, and improved drainage channels
- Developing real-time early warning systems to reduce risk to life and property during extreme events
What tools are used in water resources engineering?
Modern water resource management and engineering relies on a powerful, integrated set of technologies:
- GIS mapping software for spatial data analysis and catchment modeling
- Drone-based LiDAR surveys for high-resolution terrain and drainage mapping
- Digital Elevation Models (DEM) for accurate water flow simulation and flood mapping
- Hydrological modeling platforms such as HEC-HMS and SWMM for storm simulation
- AI-based flood prediction systems for real-time early warning and emergency preparedness
Is a hydrological survey mandatory for large infrastructure projects?
Yes, for most large infrastructure projects in India. A hydrological survey is mandatory or strongly required in the following cases:
- Highway and road projects that require drainage design and hydraulic sizing of bridges and culverts
- Residential and commercial townships above a specified development scale
- Industrial developments that require an environmental clearance from the authorities
- Any project that submits an Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) as part of approval
- Projects located in flood-prone, coastal, hilly, or ecologically sensitive areas
